
The different phases of your cycle
A woman's menstrual cycle is a complex and dynamic process regulated by a complex interplay of hormones. The cycle is usually divided into four phases, comparable to the four seasons (spring - summer - autumn - winter), each with its own specific characteristics.
The Four Phases of Your Cycle
1. Menstruation (winter): The first phase of the cycle begins on day one of menstruation and usually lasts about 3-7 days. During this phase, the uterine lining is shed and removed from the body as menstrual blood.
2. Follicular phase (spring): After menstruation, the follicular phase begins, which usually lasts about 7-14 days. During this phase, the body stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries in preparation for ovulation.
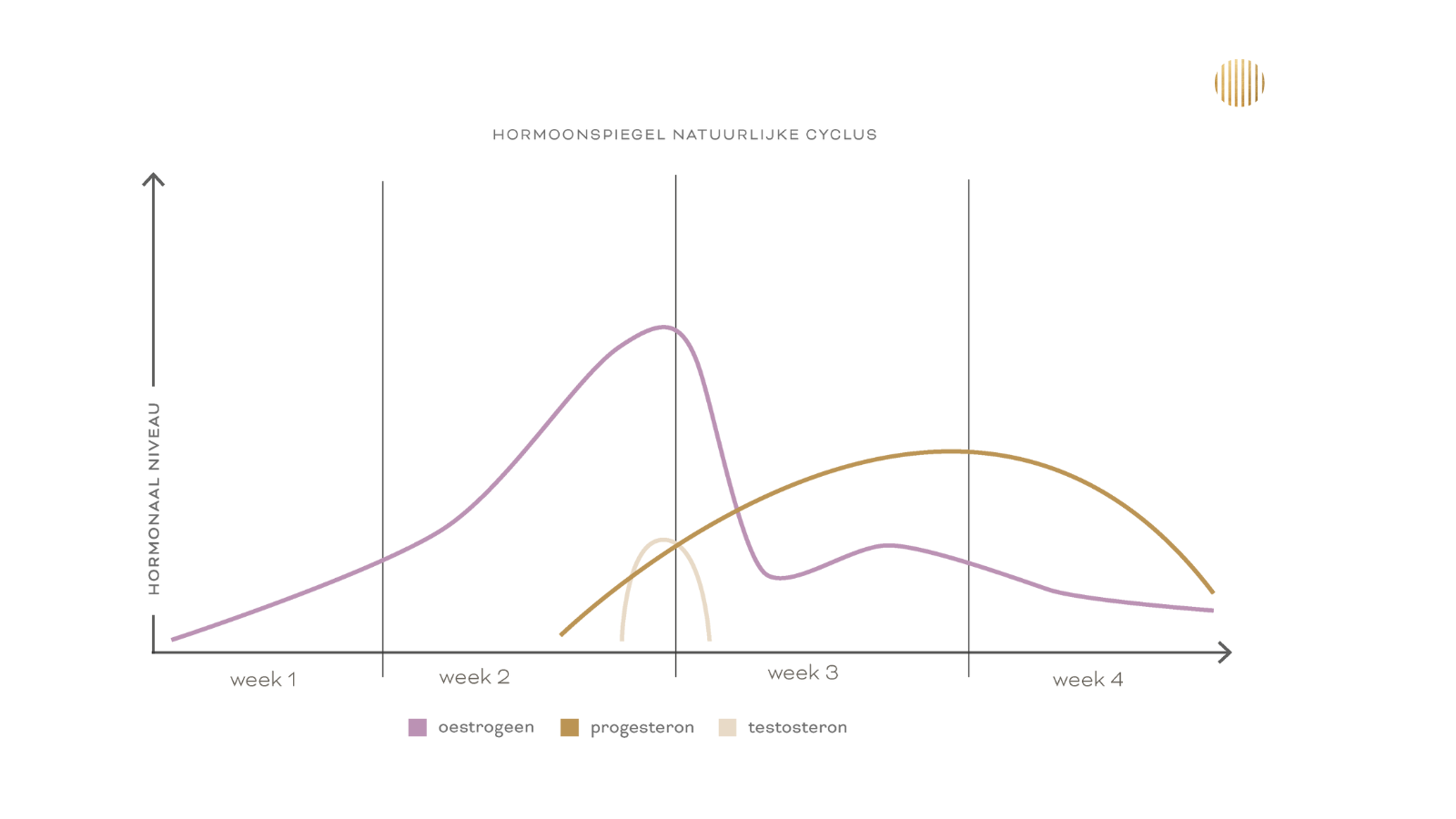
3. Ovulation or ovulation (summer): The ovulation phase usually occurs midway through the menstrual cycle, about 14 days before the start of the next period. During this phase, a mature egg is released from one of the follicles in the ovaries and is ready to be fertilized by sperm.
4. Luteal phase (fall): After ovulation, the luteal phase begins, which usually lasts about 10-14 days. During this phase, hormones such as progesterone and estrogen are produced to prepare the uterus for a possible pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, hormone levels drop, leading to the onset of menstruation and the start of a new cycle.
For optimal fertility, it's crucial that the luteal phase lasts sufficiently. This requires a high enough progesterone peak, giving the fertilized egg enough time to implant in the uterine wall. However, this phase can sometimes be too short, complicating fertilization and pregnancy. Chasteberry*, found in Pure Cycle, helps increase this peak, lengthening the luteal phase. This prepares the body for a potential pregnancy.

Your Cycle During Hormonal Contraception
Hormonal contraceptive methods , such as the pill, can alter a woman's natural menstrual cycle. Instead of going through the typical four phases of the cycle, these methods keep hormone levels constant throughout the month. In this artificial cycle, estrogen and progesterone levels remain relatively stable, which can make menstrual bleeding lighter and less painful.
On the other hand, using hormonal contraception prevents your body from producing natural hormones, which can affect various aspects of your health, such as mood, libido and menstrual pattern.
Both natural and artificial cycles have their advantages and disadvantages. It's important for women to be aware of these differences and be well-informed before making a contraceptive choice. Every woman has the right to decide which method works best for her, but it's essential to strive for a well-informed choice that takes individual needs and health into account.
Looking for natural support to balance your menstrual cycle? Discover Pure Cycle , our product specifically designed to help regulate your menstrual cycle and promote healthy hormonal balance.









